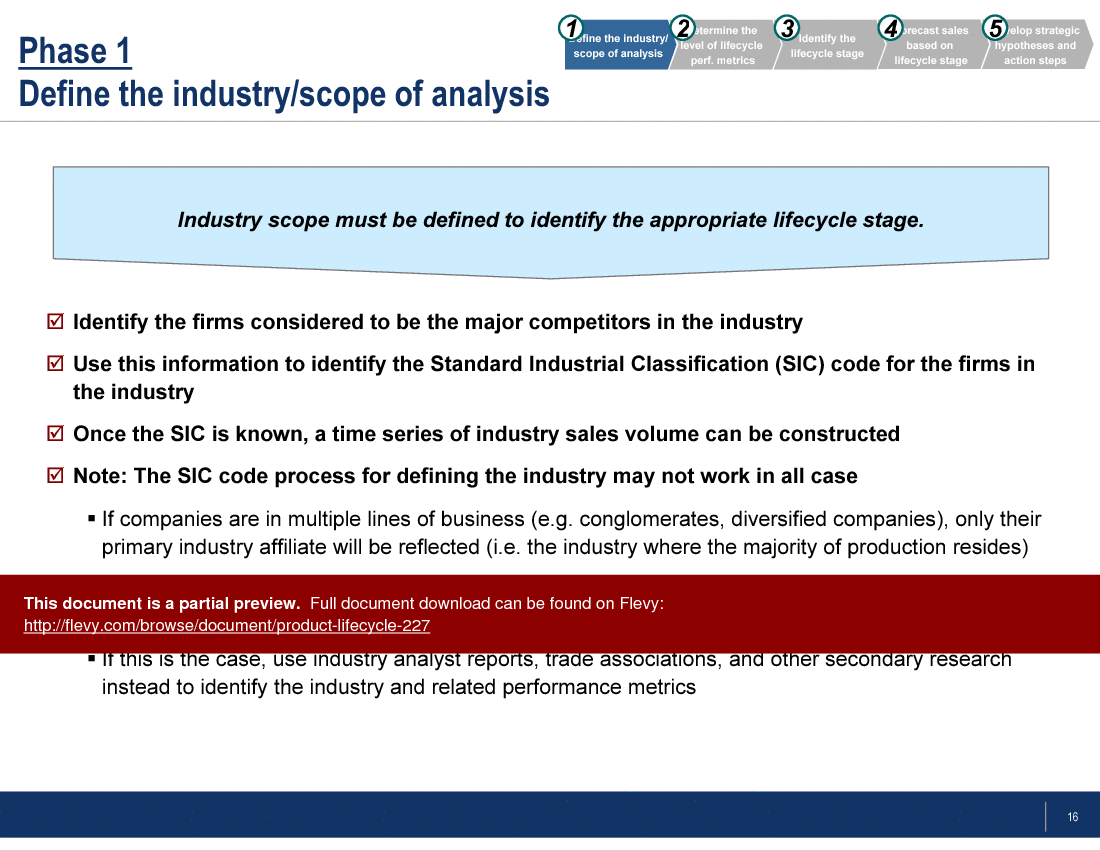
2. ARCHITECT THE RIGHT PRODUCT
What product attributes drive rapid market diffusion and consumer adoption? Tough question.
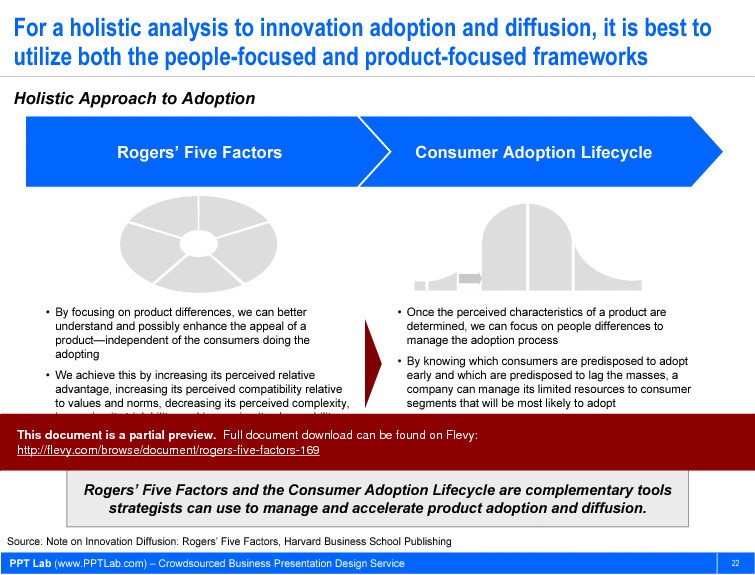
But, good thing we have the Rogers’ Five Factors framework. Credit goes to Everett Rogers, who also created the Consumer Adoption Curve.
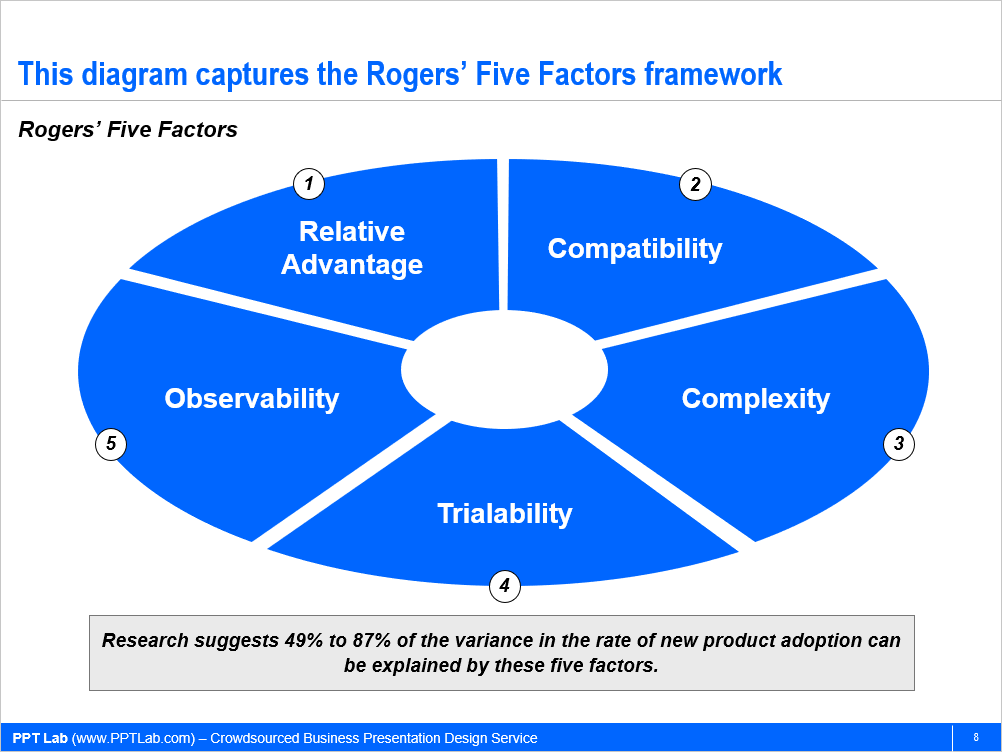
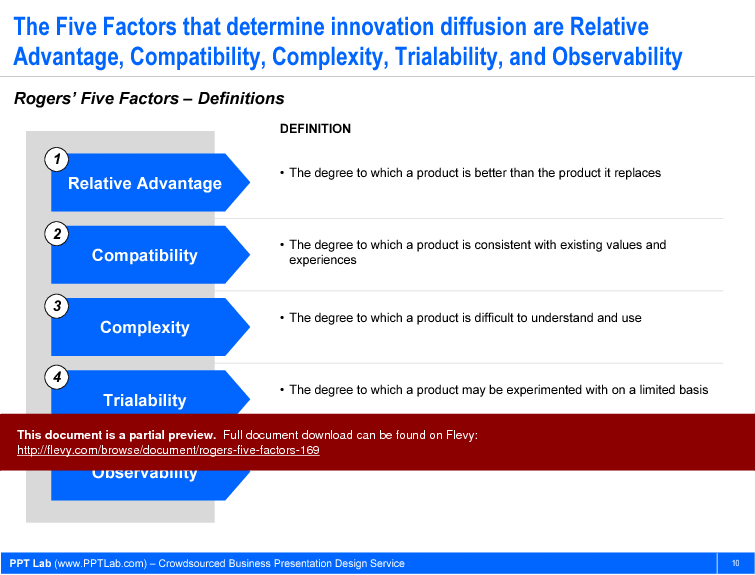
Rogers’ Five Factors proposes there are 5 product-based factors that drive adoption.
- Relative Advantage. This is the degree to which our new product is better than the incumbent. This advantage can be non-economic (e.g. social status, prestige). The greater the relative advantage, the faster the adoption.
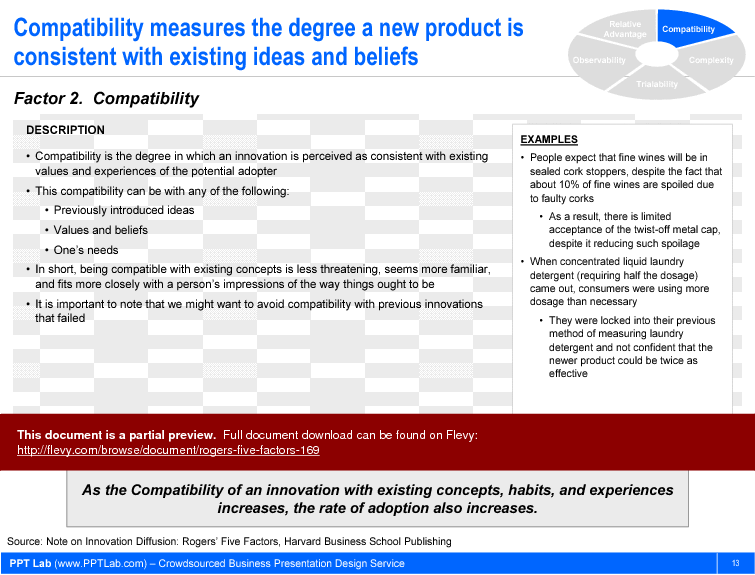
- Compatibility. This factor accounts for the degree to which our product is consistent with the customers’ existing values and experiences. The greater the compatibility, the faster the adoption.
- Complexity. This is the degree to which our product is difficult to understand and use. The primary way to overcome complexity is education, but it is important to assess how willing the customer is to be educated. The greater the complexity, the slower the adoption.
- Trialability. This factor measures the degree to which our product can be experimented with on a limited basis. This factor is most important when our product is in the early stage of its lifecycle–when uncertainty about the product’s benefits are at its highest. The greater the trialability, the faster the adoption.
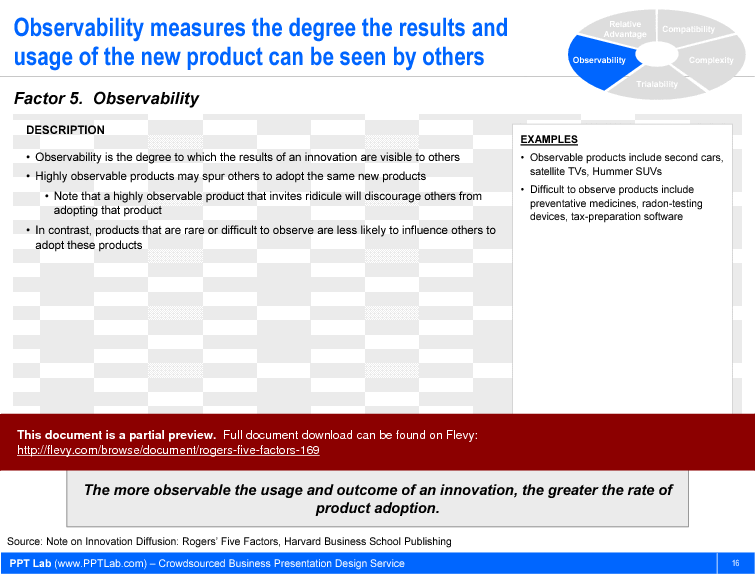
- Observability. This is the degree to which potential customers can see others using our product. For instance, highly observable products include cars and cell phones. Difficult to observe products include medicines and home appliances. Many companies leverage social media marketing–and specifically target “influencers”—to increase their observability factor. The greater the observability, the faster the adoption.
Let’s walk through an example of this analysis. Look at the telephone. Up through the late 2000s, every home had a phone. It’s something we take for granted, something that’s necessary part of our daily lives, something we can’t imagine living without. One would assume it was adopted very quickly. Yet, the reality proves otherwise...
The telephone was invented by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876. By 1900, 25 years later, it would only be found in 10% of the households in the US. By 1935, 60 years after its invention, it could only be found in 30% of households. In fact, it wasn’t until the 1980s that the telephone reached 90% of US households.
Why was the adoption rate so exceedingly slow for this wonderful, useful invention?
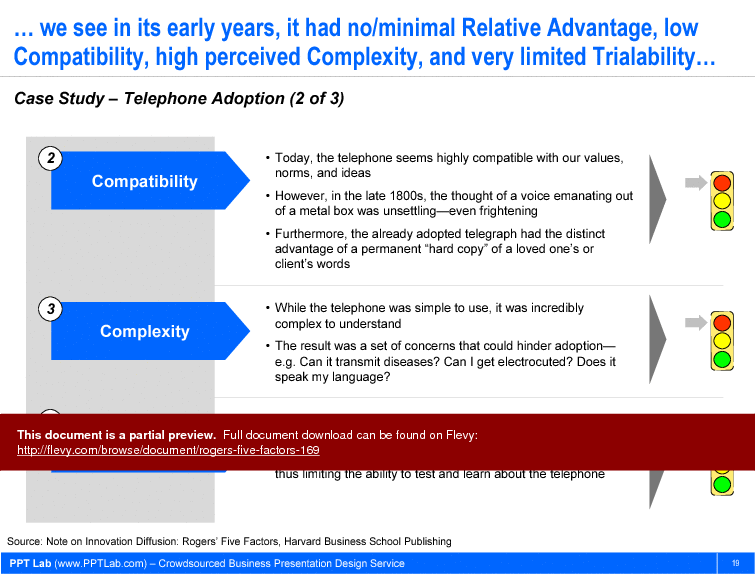
A look at the Five Factors sheds some light. The Relative Advantage for the phone was low when it was introduced. It was expensive–both installation and ongoing fees were high–and you had few people you could call. It was also highly incompatible with the norms of the time. The idea of speaking into a metal box was foreign and frightening. The technology used in the phone was incredibly Complex and difficult to understand. People wondered, can it transmit diseases? Can I get electrocuted? Does it only speak English? Trialability was low—only the very wealthy and businesses had telephones installed. In fact, in its early years, the only factor the telephone had going for it was Observability, since people could see the telephone wire running into a house.
3. UNDERSTAND THE CUSTOMER
If you are targeting the right market with the right marketing mix, have a compelling product that fosters adoption, the third essential element to analyze is the customer. What makes the customer tick? Rogers’ Five Factors touched a bit on this already, but let us take a deeper look into Consumer Psychology.
If you have a great product, but the product adoption is poor, it is imperative to understand some key concepts in behavioral economics. Here are three important principles to be cognizant of.
Principle 1. Losses Loom Larger than Gains
Every new product provides perceived gains and losses for the customer. These gains and losses need not be financial. For example, let’s say you are starting an online grocery store for your municipality. With the promise of groceries delivered to the door, the perceived gains could be convenience, time savings, and effort savings. On the other hand, you are altering the way the customer performs a certain process–buying groceries. This change will translate to perceived losses (i.e. financial and non-financial costs), which can include the inability to handpick produce and meat, delivery fees, and having to be home during the delivery window.
When we look at this objectively, online groceries is a clear superior choice. Convenience, time savings, and effort savings are great value propositions, after all.
However, when the customer evaluates options subjectively, it becomes unclear whether online groceries is still the better choice. In fact, it is likely the customer views online grocery shopping as the poorer choice. This is because losses loom larger than gains.
A consumer has an inherent Consumer Bias. This bias weighs a loss three times that of a benefit. To put it another way, the objective value of a gain needs to exceed the objective value of a loss by three times for the customer to perceive the new product as better than the existing.
What's the solution? One tactic is to apply "the 10X rule."
If losses loom larger than gains, then we need to create a product where the gains greatly dwarf the losses. Create one where the benefits are 10X that of the losses, so that all economic and psychological switching costs are overcome. This is also known as Andy Grove’s 10X Rule. Andy Grove, Intel’s third employee and former CEO, had stated, for widespread adoption, a new product has to offer a 10X improvement over the incumbent product.
Of course, this strategy is easier said than done.
Principle 2. Reference Points Matter
The second principle to understand is different people have different reference points. These reference points matter. The reference point simply refers to the person’s current state of being.
Continuing our online grocer example, the reference point of a typical customer is someone who currently goes to the physical supermarket to pick up groceries. This process may already be part of the customer’s weekly routine. Gains and losses are relative to this state of being.
For two people with different reference points, a gain for one person may be perceived as a loss for the other. To illustrate this concept, let’s look at the price of gas. Assume the average price for a gallon of gas in the US is $3, whereas it’s $10 in the UK. If a US customer came upon a gas station charging $6.50/gallon, she would be furious. If a UK customer came upon the same situation, she would be ecstatic. (Also, note that even though the objective difference is the same for both customers, the US customer’s sentiment would be more affected than that of the UK customer, because losses loom greater than gains.)
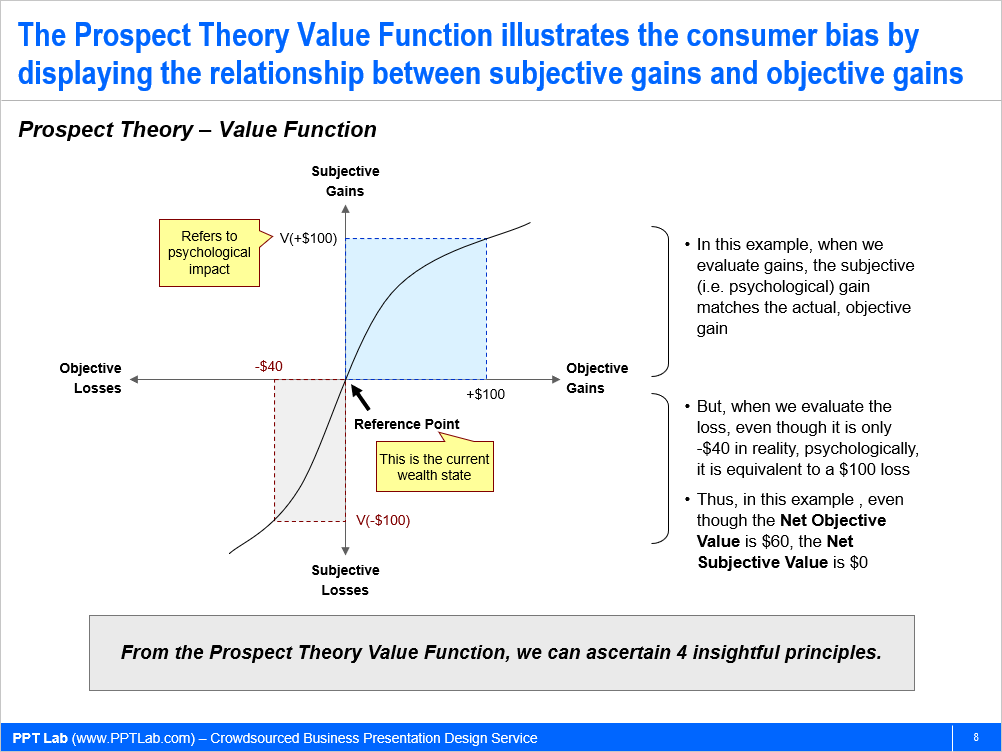
By understanding your customer’s reference point, you can determine her perceived gains and losses. In most cases, your reference point is different from that of your customer. This is because you have already used and experienced your product, whereas your customer has not. Your product has become part of your state of being. This disparity in judgment is captured in the concept known as the Innovator’s Curse.
What's the solution? One effective strategy is a reference point pivot.
Since reference points dictate how customers perceive gains and losses, it makes sense to seek out customers with favorable reference points. Think about it this way. In one market, your product may have fulfilled the 10X Rule. In another, your same product may be perceived as 10X worse!
During its earlier years, Walmart opened stores only in rural areas to compete against local mom and pops. Compared with these incumbent retailers, Walmart was a clear 10X improvement. If Walmart had started off launching stores in metropolitan areas instead, where large department store chains were already established, Walmart’s growth would have been hindered.
Ideal markets are ones filled with first time buyers. For the first time buyer, her reference point is neutral. She doesn’t have any preconceived biases over existing benefits lost and new costs incurred, because she doesn’t currently use the incumbent solution. Thus, for many products, it is easiest to launch in emerging markets. This is because emerging markets (e.g. BRICS nations) are filled with first time buyers.
Principle 3. Endowment Effect
According to the Endowment Effect, people value items in their possession (i.e. part of their endowment) more than items not in their possession. This is because people are loss averse.
This behavior sheds some light on why losses loom larger than gains. If a customer is already accustomed to an existing product or existing way of doing things, it becomes hard for her to give that up and change–even if the alternative presents greater benefits.
An easy and common method companies leverage to take advantage of this psychological principle is to offer free samples, so the customer gets hooked on their products. Once the customer begins using the product, he or she will appreciate the benefits it offers and is likely to spend money to retain these benefits. This is, in essence, an example of Reference Point Pivot.
Similarly, a popular business model adopted by many Internet SaaS companies is the “freemium” model. In the freemium model, the customer is first presented with a free version of the product. Then, the customer is offered (or forced) to a premium version.
For more information on Behavioral Psychology, take a look at these resources:
4. OPTIMIZE THE CUSTOMER JOURNEY
In most cases, the product you’re selling is not an impulse purchase. The path to purchase is a long process–it’s a journey that can take from several days to several months. This journey is captured in a framework developed by McKinsey & Co called the Customer Decision Journey.
The Customer Decision Journey proposes that the customer goes through four phases in a cyclical process. Each phase represents a potential marketing battleground where companies compete for the customer’s purchase and loyalty.
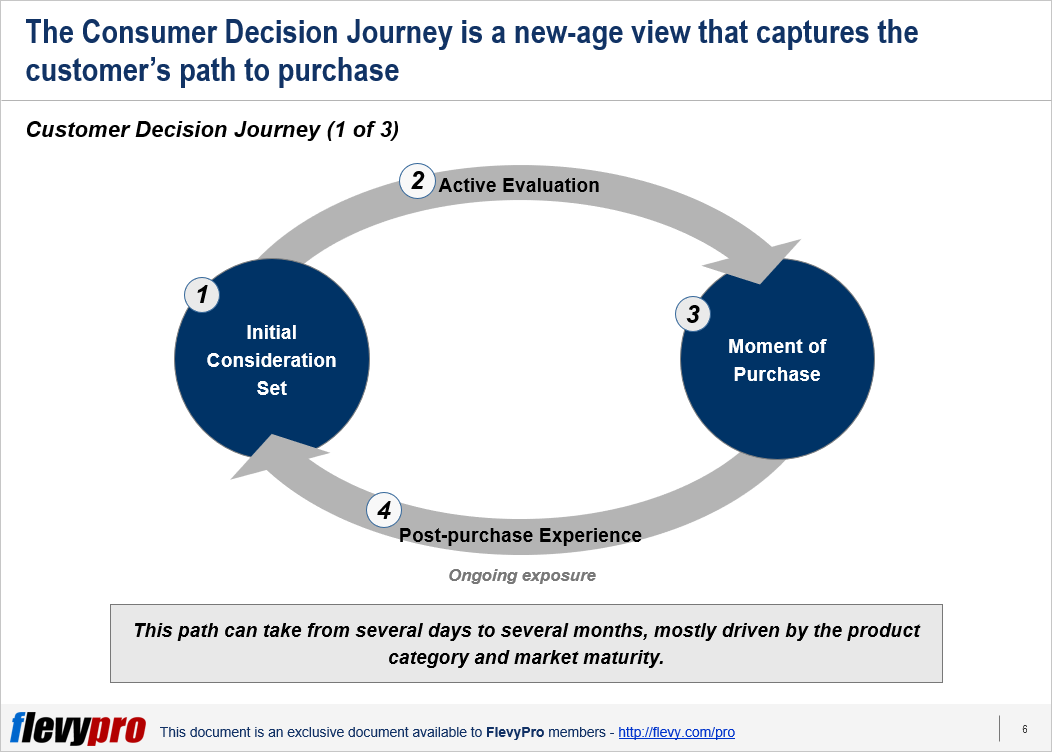
These phases along the customer’s journey are:
- Initial Consideration. When the customer first conceives the notion of buying a product, she will develop an initial set of brands to consider buying. Brands in the initial-consideration set are three times more likely to be purchased than brands that aren’t in it. This means that Brand Awareness is vital. In this phase, we should focus on push marketing.
- Active Evaluation. In the evaluation phase, the customer is seeking information and shopping around to make an informed purchase decision. She will ask for recommendations from friends and family, read reviews online, go to the store to test out products, and so forth. This phase empowers both the customer and the company. How are companies empowered? Companies have the opportunity to enter the consideration set—and even force out companies in the Initial Consideration Set. Big brands can no longer take their position for granted. In fact, due to this phenomenon, we have seen the successful rise direct-to-consumer startups. A popular influencer or creator with a small team can launch their own brands and compete against established, billion dollar companies. With increased online and social presences, companies are increasing the number of touch points with the customer—thus increasing their influence over the customer’s purchase decision in the Active Evaluation phase.
- Moment of Purchase. This is the point in time when the customer goes to the retailer and makes the purchase. Even at this late stage of the journey, companies can still influence the purchase. This is done through in-store marketing and influence of store salesmen.
- Post-purchase Experience. After the purchase, the customer builds expectations based on her experience that will impact her next purchase journey. This creates the circular nature of the journey. In this phase, our goal is to foster customer loyalty, which will drive repeat purchases and word-of-mouth marketing. Likewise, if the customer is dissatisfied with the purchase, she will become a negative influence on the purchase decisions of others. This is not limited to her immediate circle of friends and family either. For instance, she can post a negative review on a prominent website, which will be read by countless potential customers in the Active Evaluation stage.
If our goal is to reach an emerging market, there are certain nuances that should be highlighted and understood. Though the overarching process is the same, the emphasis in marketing is different when comparing a customer in an emerging market versus a customer in an established market. For instance, in an established market, customers often rely on online reviews when making purchase decisions. In emerging markets, online sites are not yet trusted by the customer. Learn more about this topic in this article: Craft a Successful Strategy for Emerging Markets.
For more information on Customer Journey, take a look at these frameworks:
5. MAXIMIZE THE ONLINE EXPERIENCE
The Internet is becoming more and more crucial in the Customer’s Decision Journey. Because of the Internet, the number of customer touch points has increased significantly.
In the online experience, there are 5 categories of customer touch points. They have varying levels of importance along the path to purchase:
- Paid. This category includes paid display and search advertising.
- Social. This category refers to interactions with the customer through social media (namely, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Youtube).
- Email. Email marketing typically takes the form of recurring newsletters. Newsletters are essentially the online form of the offline store circular.
- Referral. This category refers to external websites that “refer” customers to your website.
- Direct. This refers to your own website. It encompasses the customers who go directly to your website.
Here is the typical flow of online interaction with the customer through her journey. At the start, the goal is to create Brand Awareness. This is typically achieved through investments in paid advertisements. As the customer begins to actively evaluate her various product choices, Social and Email begin to play a more important role. Through social media, companies can directly engage and influence customers. Email marketing is an effective method of building rapport with a customer. Once a customer has subscribed to our newsletter, we can send regular newsletters to constantly remind her of our company and products. The customers that are most likely to make a purchase are Referral and Direct visitors. Afterwards, in the post-purchase phase, Social and Email continue to play important roles in nurturing that customer bond.
Of course, the relationship between the touch point and decision journey varies by industry and varies by geography.
Source: Product Lifecycle, Rogers' Five Factors, Psychology of Product Adoption
[Full source materials below]
|
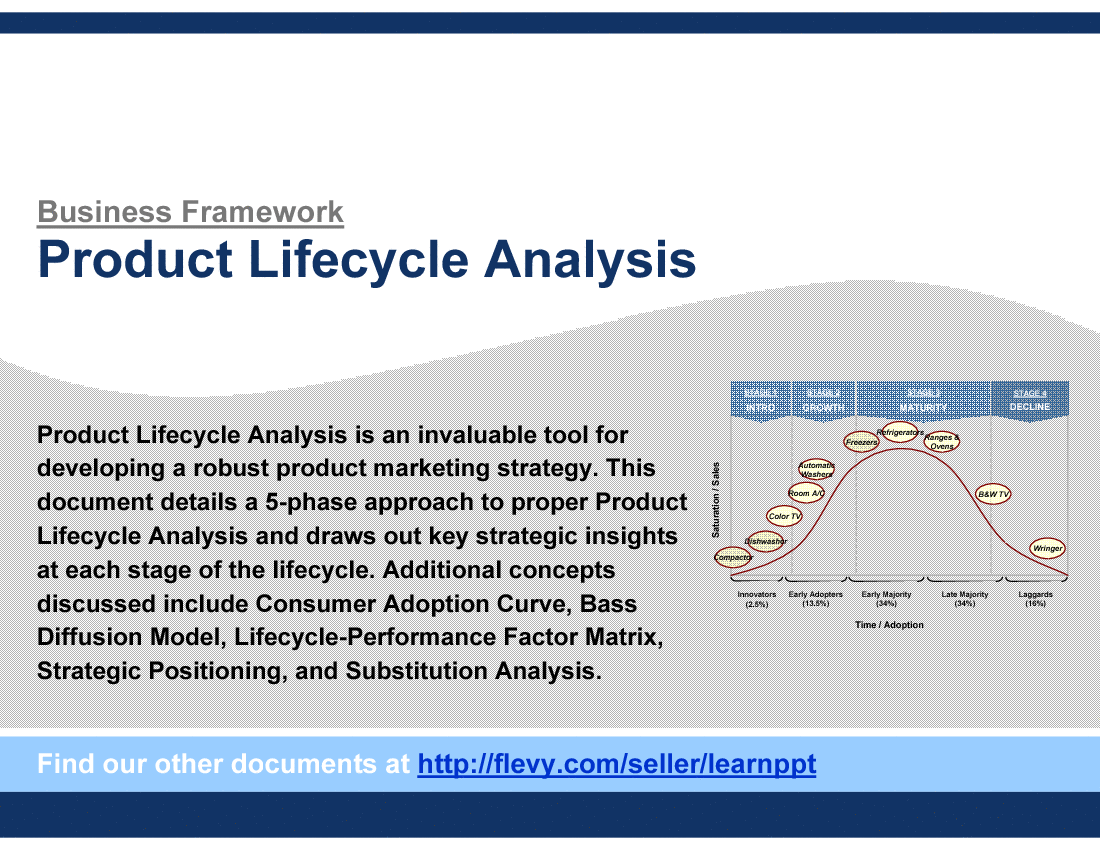
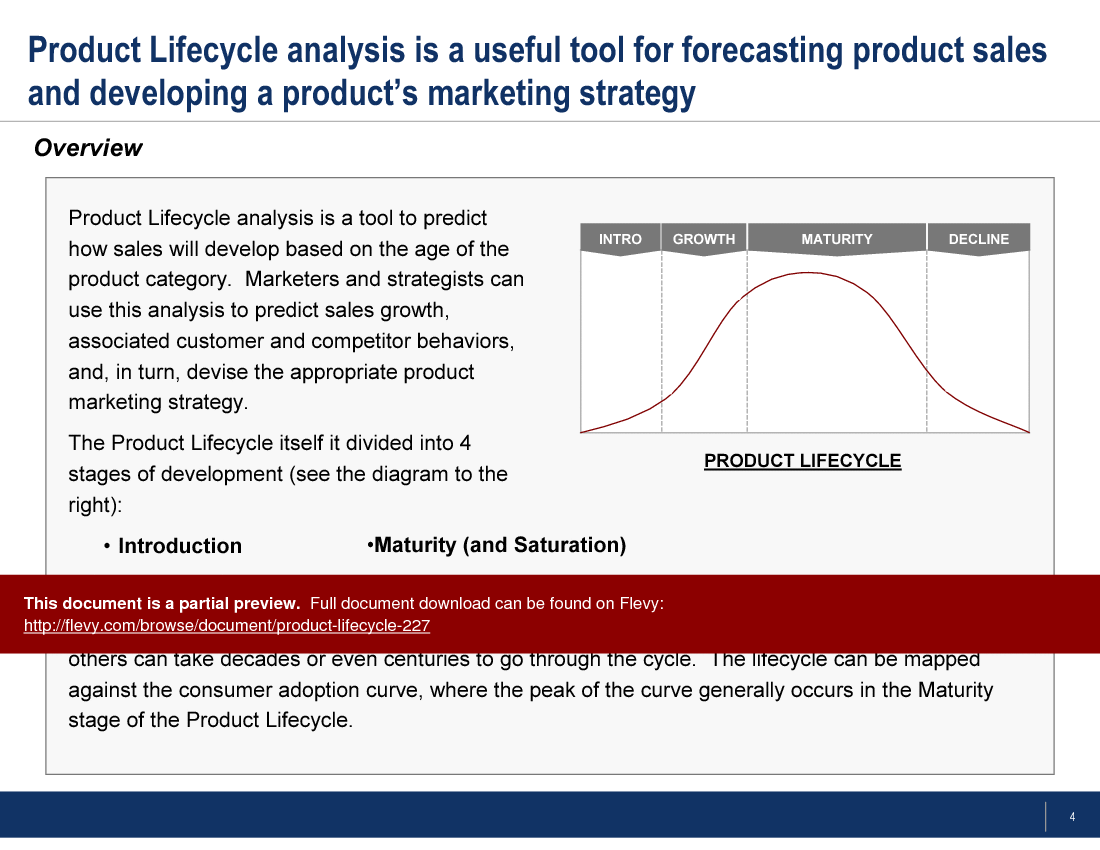
Product Lifecycle
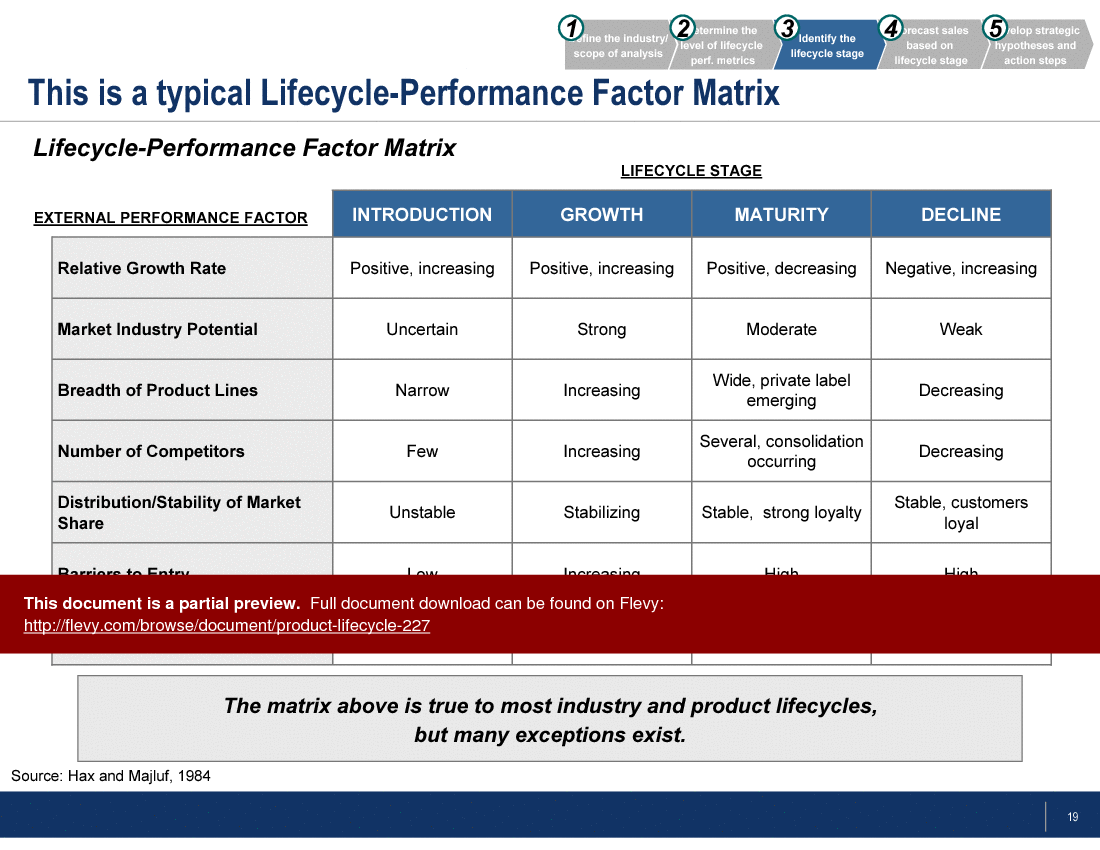
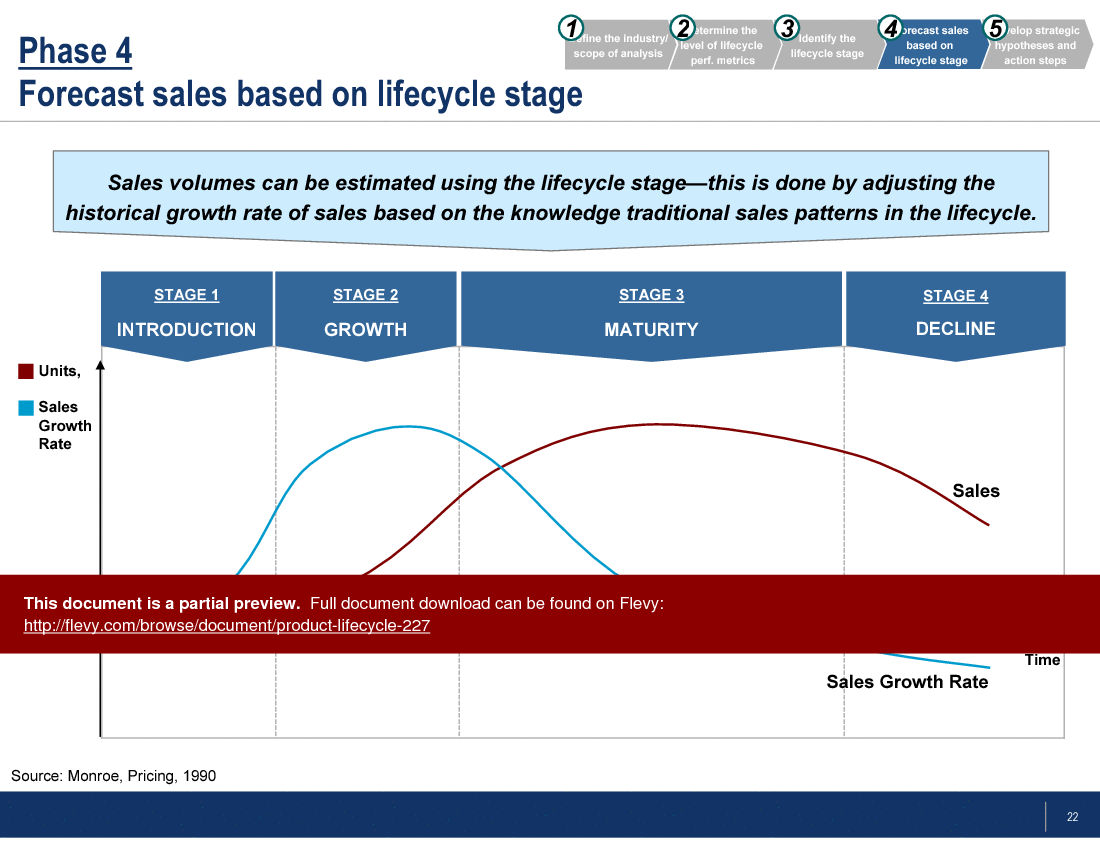
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|
|
Product Lifecycle
All products mature through 5 stages of development. The length of each period varies tremendously. Some products have very short cycles, whereas others can take decades or even centuries to go through the cycle. This framework details a 5-phase approach to proper Product Lifecycle Analysis and draws out key strategic insights at each stage of the lifecycle. Specific topics covered include the Consumer Adoption Curve, Bass Diffusion Model, Lifecycle-Performance Matrix, Strategic Positioning, among others. |
$39.00
|
|
Rogers' Five Factors
Rogers' Five Factors is a framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations. Whereas the Product Lifecycle (above) focuses on people, Rogers' Five Factors is focuses on the product. This framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors. This document explains the Rogers' Five Factors, provides examples, shows how to use this framework in conjunction with the Production Adoption Lifecycle. |
$39.00
|